How to use Qualify Row_number in BigQuery?
Contents
ROW_NUMBER() function in BigQuery
Row_number is a Numbering function which is a subset of Analytic function in BigQuery. In the analytic function, the OVER clause should be included to define a window of rows within a query result set. For each selected window of rows, Row_number function assigns a unique number.
Syntax of Row number in BigQuery
|
1 2 |
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITIONED BY <column_reference> ORDER BY <value_expression> ASC/DESC) |
- PARTITIONED BY: breaks up the input rows into separate partitions, over which the analytic function is independently evaluated.
- column_reference is a column name which is used to define the window of the rows.
- ORDER BY: Defines how rows are ordered within a partition.
- value_expression is a column name that is used for sorting the rows within each partition.
Filtering results with the QUALIFY clause
The QUALIFY clause is used to filter the results of analytic function. As mentioned earlier, Row number functions assigns the unique number(1,2,3..) for each row in the partition, From that result set, Qualify filter the rows based on condition.
|
1 2 |
QUALIFY ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITIONED BY <column_reference> ORDER BY <value_expression> ASC/DESC) <filter_condition> |
Example
Let’s understand Qualify row_number with example. We have a table house_rent_details in BigQuery. It contains the monthly rent details of the houses as below. Here rc_fin_test_tables is a dataset name. The columns of this table are Property_id, Address, Monthly_rent_in_dollars and City.

From this table, we want to find the low rent house details for each city. The column reference for partition is city. The sort_expression can be defined using the Monthly_rent_in_dollars column.
Let’s write the query with the Row number function. It will assign the unique integer number for each row within a partition. To sort the rent in ascending order within each partition, we are giving the ORDER BY clause in the query.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT Property_id, Address, Monthly_rent_in_dollars, City, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY City ORDER BY Monthly_rent_in_dollars ASC) as Row_Number FROM rc_fin_test_tables.house_rent_details; |
Output
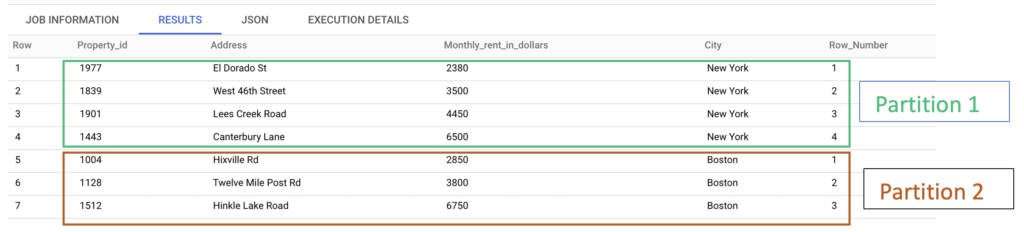
After executing the query, we can see that each city is considered as a partition. For example, One partition has the New York city. Another partition has the Boston city.
In each partition, the rows are sorted in ascending order based on the Monthly_rent_in_dollars values. After that the row numbers are assigned to each row in the partition.
Filter the results using QUALIFY Clause
Now we can apply the Qualify clause to filter the results based on row number. Since we want to find the low rent house details for each city, we can fetch only the row which has row number as 1. Let’s write a query with Qualify as below
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT Property_id, Address, Monthly_rent_in_dollars, City FROM rc_fin_test_tables.house_rent_details Qualify ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY City ORDER BY Monthly_rent_in_dollars ASC) = 1; |
Output
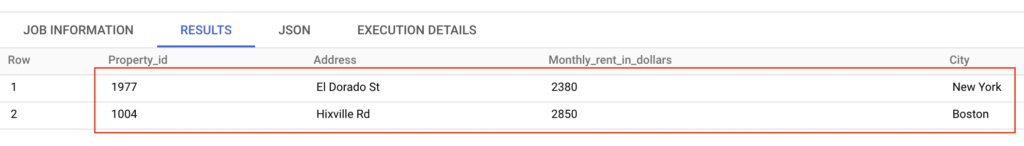
Finally the QUALIFY clause returned the low rent house details for each city. Similarly we can get the highest rent house details for each city. To get that results, we just need to sort the rent details in descending order.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT Property_id, Address, Monthly_rent_in_dollars, City FROM rc_fin_test_tables.house_rent_details Qualify ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY City ORDER BY Monthly_rent_in_dollars DESC) = 1; |
Output
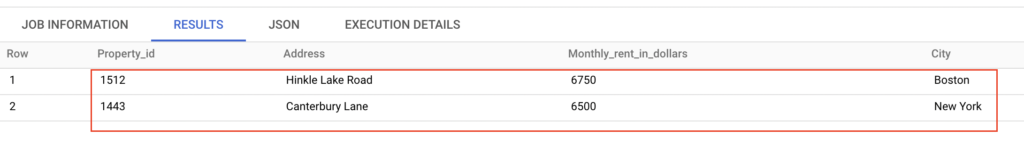
Recommended Articles
- How to flatten an array using UNNEST function in BigQuery?
- Regexp_replace function in BigQuery with examples
- How to use Qualify Row_number in Teradata?
- How to use ROW NUMBER function in Hive?
- Row_number function in Oracle with examples
