How to create an external table in BigQuery?
Contents
External table in BigQuery
External Data Sources
The data which is not stored in the BigQuery storage is called as External (Federated) data sources. To query the data from those sources, we can create an External table in BigQuery. The following external data sources can be used in BigQuery
- Bigtable
- Cloud Spanner
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Storage
- Drive
External table
An External table is a standard BigQuery table. The table metadata is stored in the BigQuery storage. But the data itself is resides in the external source. In this tutorial, we will create a BigQuery External table to query the data from Google Cloud storage(GCS).
Create External table in BigQuery
The CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE statement create a new external table in BigQuery.
Syntax
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] EXTERNAL TABLE [ IF NOT EXISTS ] table_name [( column_name column_schema, ... )] [WITH CONNECTION connection_name] [WITH PARTITION COLUMNS [( partition_column_name partition_column_type, ... )] ] OPTIONS ( external_table_option_list, ... ); |
- OR REPLACE – It replaces any external table with the same name if it exists. It cannot appear with IF NOT EXISTS.
- IF NOT EXISTS – If the table is already exist with the same name, the CREATE TABLE statement has no effect. It cannot appear with OR REPLACE.
- table_name – The name of the external table
- column_name – The name of the column in table.
- column_schema – The data type of the column in table. BigQuery deducts the schema automatically if it is not specified.
- connection_name – It specifies the connection resource that has credentials to access the external data.
- partition_column_name – The name of the partition column
- partition_column_type – The data type of the partition column
- external_table_option_list – It defines the external data properties such as location, format, delimiter and so on. Please refer here for more details.
Example
For this example, we have a sample CSV file in Cloud storage. As we shown below, we have a Cloud storage bucket rc-marketing. Under that we have a folder SEO which contains the file SEO_daily_0614.csv.
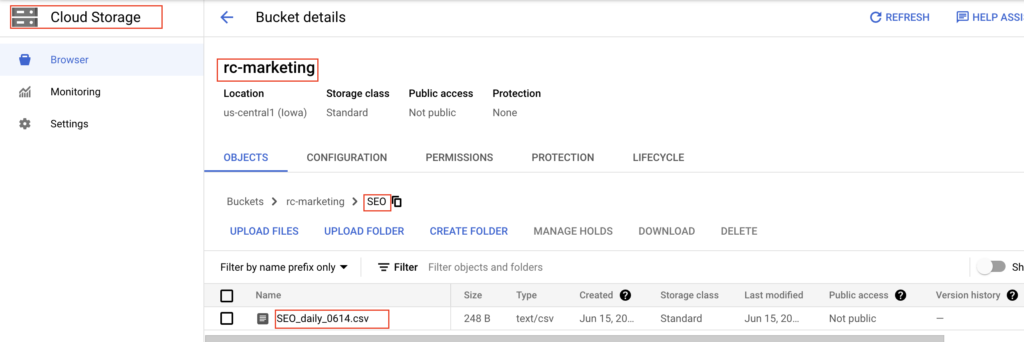
The CSV file contains Search Engine Optimization(SEO) data of the website. It contains the header row as well. The URI of the file is gs://rc-marketing/SEO/SEO_daily_0614.csv. Let’s check the data using gsutil cat command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
rc_user_1@ls-server ~ % gsutil cat gs://rc-marketing/SEO/SEO_daily_0614.csv Device_Type,Total_Sessions,Unique_Vistor,Total_Page_Views,Avg_Visit_Duration,Bounce_Rate,Dat_Updated Desktop,12383,11500,14230,2.15,65.27,2022-06-14 Mobile,14290,12003,15783,3.88,44.15,2022-06-14 Tablet,11345,10738,12445,2.44,35.71,2022-06-14 |
Now we can create the BigQuery External table for this cloud storage file. Let’s write the CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE statement as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE rc_marketing_tables.seo_analytics OPTIONS( format = 'CSV', uris = ['gs://rc-marketing/SEO/SEO_daily_0614.csv'] ); |
The format and URI of the cloud storage file is mentioned in the options. As mentioned earlier, BigQuery automatically deducts the schema using external data sources. So we didn’t mention the column name and data types.
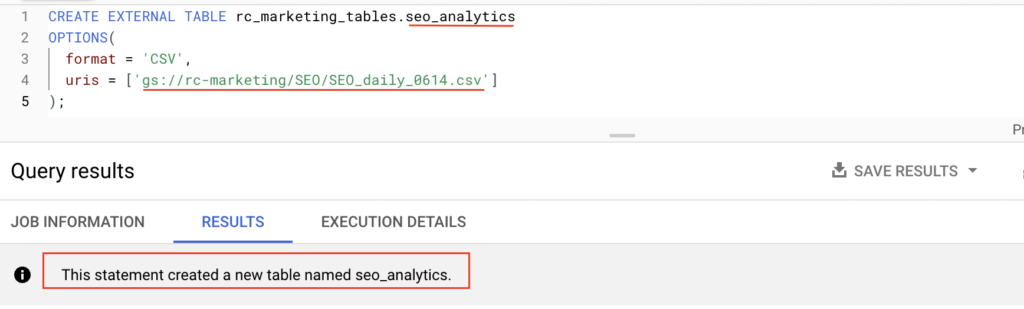
As we shown above, the Create external table statement is created the table seo_analytics in BigQuery. Here rc_marketing_tables is a dataset name.
Query the data from BigQuery external table
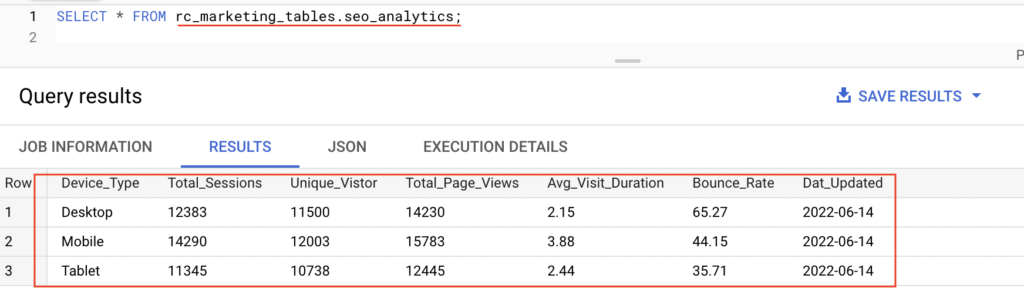
Using Select statement, we are able to query the data from the external table seo_analytics. Actually it reads the data from the cloud storage file. If we delete the external data source file SEO_daily_0614.csv, the table will return zero rows.
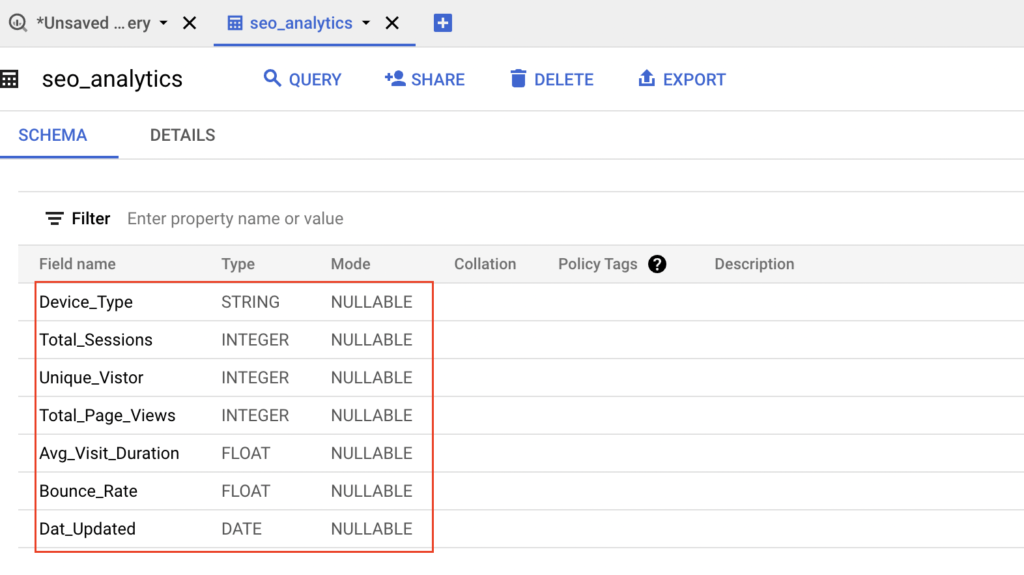
Next we can verify the column details of the table in BigQuery. As we shown below, BigQuery automatically mapped the respective data type to the columns.
Create external table with table schema
The table schema can be explicitly mentioned in the create external table statement as below. The column name and its data types are mentioned as per the external data source. Additionally we need to skip the header row (Device_Type,Total_Sessions,…..) while reading the data. For that, we set the option skip_leading_rows as 1.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE rc_marketing_tables.seo_analytics( Device_Type STRING, Total_Sessions INT64, Unique_Vistor INT64, Total_Page_Views INT64, Avg_Visit_Duration DECIMAL, Bounce_Rate DECIMAL, Dat_Updated DATE ) OPTIONS( format = 'CSV', skip_leading_rows =1, uris = ['gs://rc-marketing/SEO/SEO_daily_0614.csv'] ); |
Similarly we can create the external table to query the data from other external data sources.
Recommended Articles
- How to create a view in BigQuery?
- Create table as Select, Create table Copy and Create table Like in BigQuery
- Create a Hive External table on Google Cloud Storage(GCS)
